Current Status
Deployed across development, staging, and production environments, enabling rapid iteration and refinement. Recent work has automated data ingestion pipelines so that core datasets are refreshable, improving reliability and timeliness.
Future Development
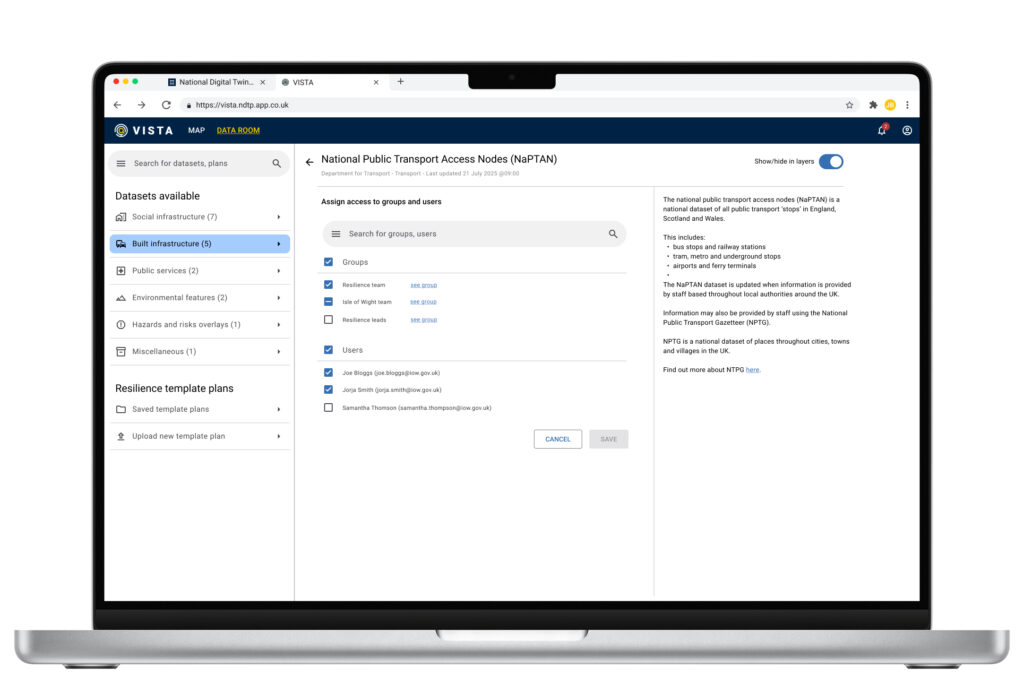
Ongoing work (from August 2025) is focused on expanding data sources, developing new user-aware data access models, and building the “data room” concept to give crisis responders quick, controlled access to relevant datasets. Future versions will continue to strengthen multi-agency collaboration and scenario planning.

Overview
What it is
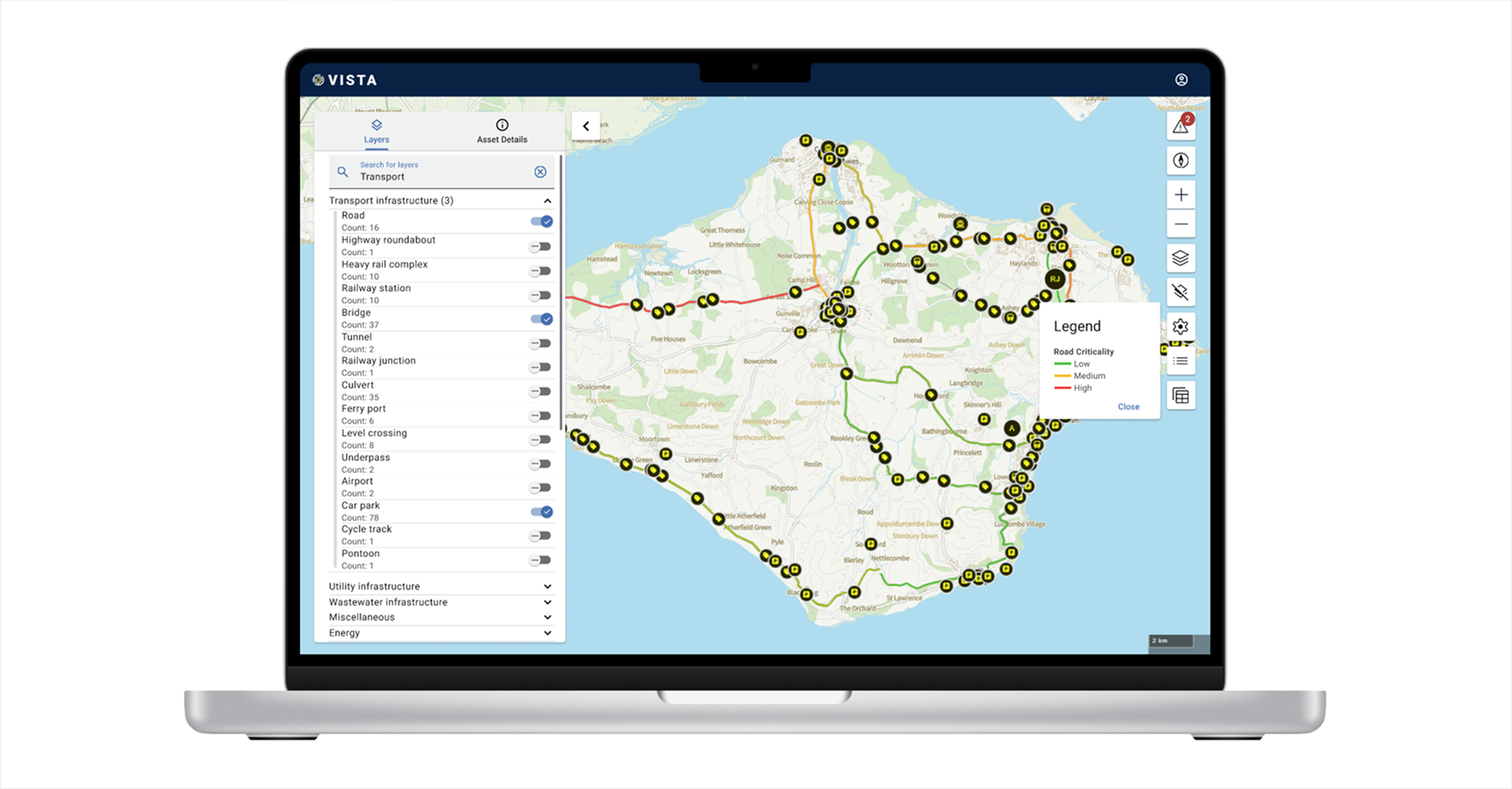
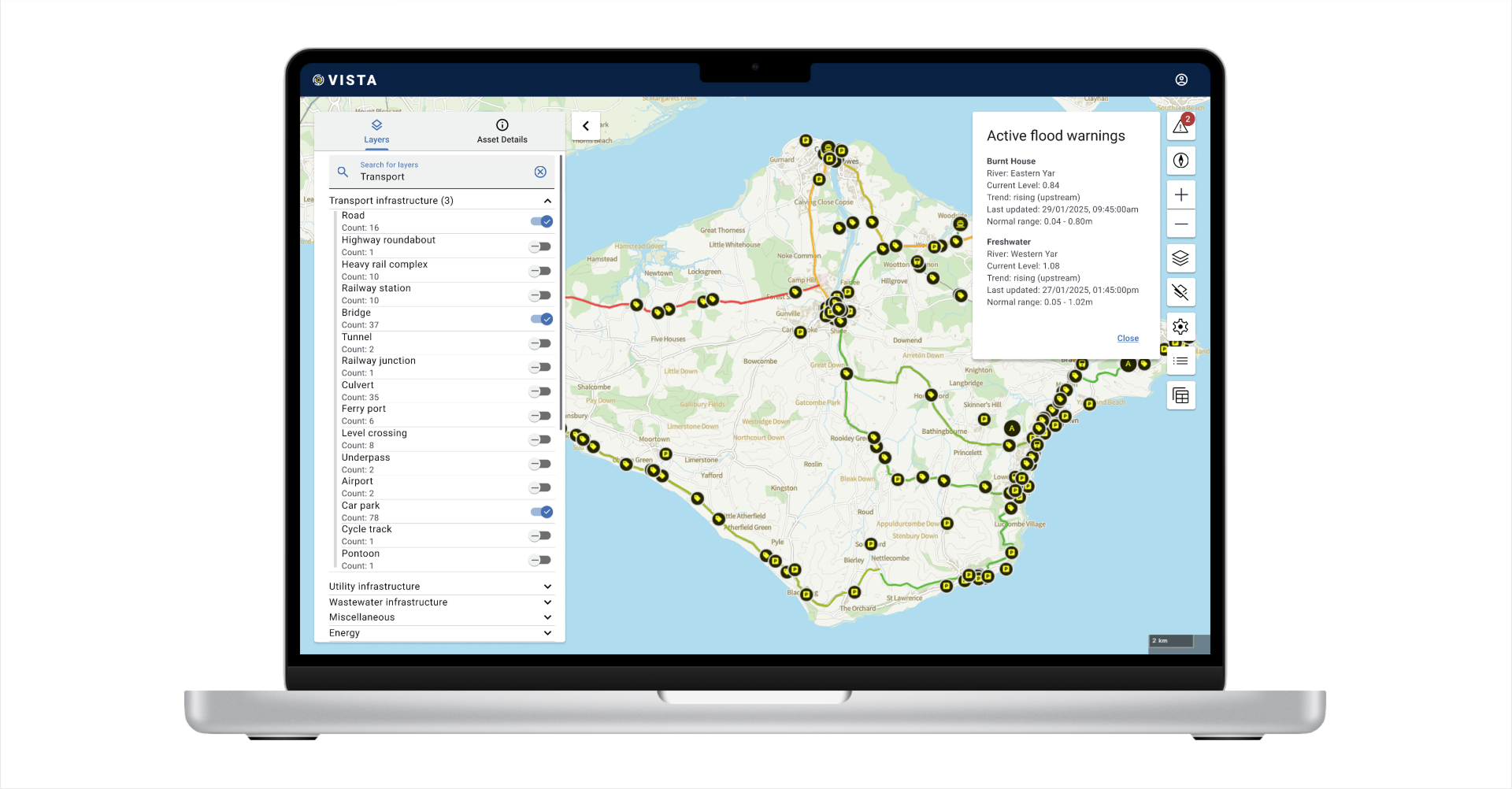
VISTA is a digital mapping tool designed to assess, visualise, and simulate cascading asset failures during emergencies. It enables real-time monitoring of infrastructure dependencies, illustrating how disruptions to key assets—such as roads, energy grids, and healthcare facilities—affect interconnected services and communities.
In addition to assessing failures, VISTA provides predictive capabilities, allowing users to simulate a range of emergency scenarios. By integrating real-world and simulated data, VISTA enables proactive planning, helping emergency responders, infrastructure managers and policy officials anticipate how disruptions propagate and optimise response efforts before incidents occur.
What problem it addresses
Emergency planning often lacks a clear, data-driven understanding of asset interdependencies, leading to delayed responses and inefficiencies. Currently, asset impact assessments are fragmented across different organisations, requiring manual collation of data under time constraints. VISTA centralises and visualises these dependencies, ensuring stakeholders can quickly assess vulnerabilities, predict cascading failures, and plan mitigations accordingly.
How it contributes to the National Digital Twin vision
VISTA is testing the ability of the National Digital Twin Programme’s (NDTP) Integration Architecture (IA) to ingest a wide range of data sources, including data from sensors. It is also examining how possible scenarios are reflected in the Information Exchange Standard (IES) to allow for the output of simulations to be brought together with other data sources to support decision-making.

Who we are working with
Lead stakeholders & collaborators:
- Department for Transport (DfT) – Key Strategic partner
- Isle of Wight Council – Key Strategic partner
- Emergency services
- Utility providers
- Island Roads (Highways PFI)
- IoW NHS Trust & Public Health

Why we are doing this
1. Strengthening NDT’s Capabilities
VISTA is a key testbed for enhancing NDTP’s open-source infrastructure. Through this demonstrator, we are:
- Testing the Integration Architecture’s (IA) ability to handle large-scale geospatial data ingestion.
- Developing the Information Exchange Standard (IES), standardising data models for infrastructure dependencies and possible scenarios.
- Expanding API capabilities for real-time data visualisation and multi-agency collaboration.
- Improving scalability, ensuring the system can support larger, more complex asset networks.
2. Addressing Real-World Infrastructure Resilience Challenges
- Provides a clear understanding of cascading asset failures, helping emergency planners anticipate knock-on effects of infrastructure failures.
- Optimises crisis response coordination, allowing agencies to quickly assess the wider impact of asset loss or degradation.
- Facilitates proactive risk management, supporting climate resilience planning for extreme weather events, flooding, and transport disruptions.
- Enhances collaboration between stakeholders, enabling local authorities, emergency services, and infrastructure operators to share and act upon real-time data.

Key Innovations & Next Steps
Following the November 2024 redevelopment of VISTA, several major improvements are now (August 2025) underway in three areas:
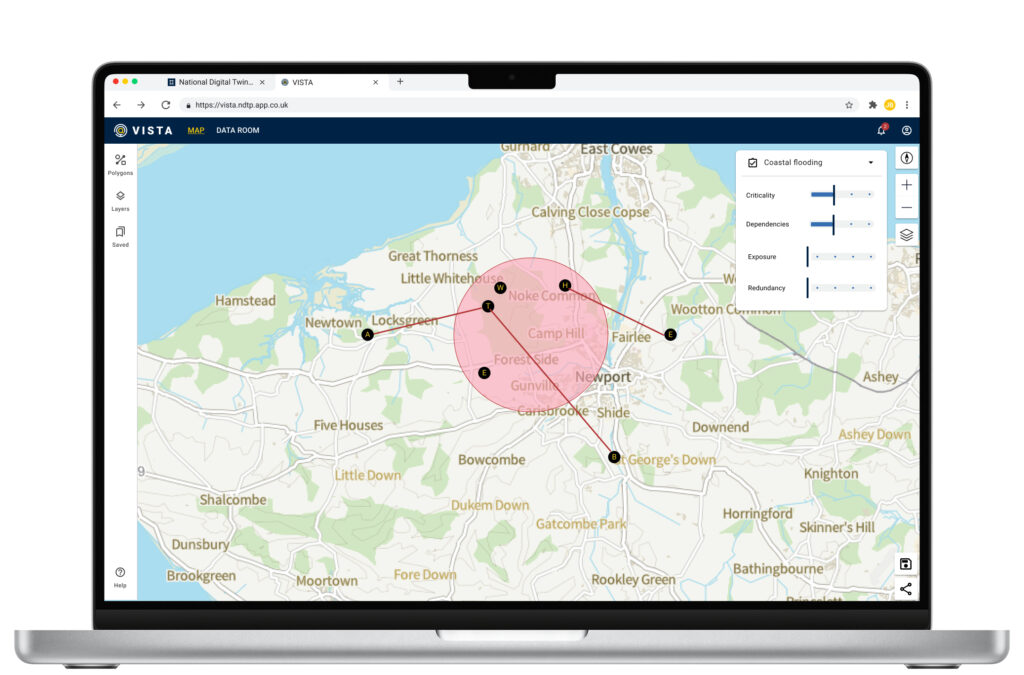
- VISTA Asset Score — a new scoring framework to understand asset resilience across four dimensions: criticality, dependency, exposure, and redundancy. This aligns with established UK emergency planning and resilience language (e.g., Civil Contingencies Act, DEFRA SEMD, EA flood maps).
- Redesigned front end — including the Data Room, improved mapping and visualisation, and faster onboarding of users during an incident.
- Refreshable data sources — automation of ingestion and update cycles, ensuring that datasets remain current and can be trusted in live response situations.

Technical Details
Architecture & Frameworks used
- Built using NDTP’s IA for secure, interoperable data sharing.
- Developed as a cloud-hosted, geospatial analytics platform, ensuring accessibility across agencies.
- Incorporates advanced GIS rendering capabilities, supporting high-resolution infrastructure mapping.
Where to Find the Code
VISTA is currently being developed in private and an open-source repository will be made available late 2025.
Additional tools, documentation, and codebases will continue to be released and updated on a regular basis as work progresses.
In the meantime, you can explore existing resources via the NDTP GitHub organisation.

Get Involved
There are multiple ways to engage with VISTA, whether you are part of government, emergency response, healthcare, industry, academia, or the technical community:
Collaboration – Government bodies, emergency response teams, and healthcare providers can contribute data, expertise, or funding to expand VISTA’s capabilities.
Adoption – Organisations can adopt or adapt VISTA for their own secure data-sharing needs, ensuring the tool is reused and extended for maximum impact.
Testing & feedback – Organisations and individuals can validate use cases, test functionality, and provide feedback to improve usability and effectiveness.
Knowledge sharing – Contributions to best practices, case studies, and policy recommendations are encouraged to guide future expansions.
If you’re interested in collaborating, adopting, or contributing, get in touch via ndtp@businessandtrade.co.uk or explore the open-source codebase on GitHub.


